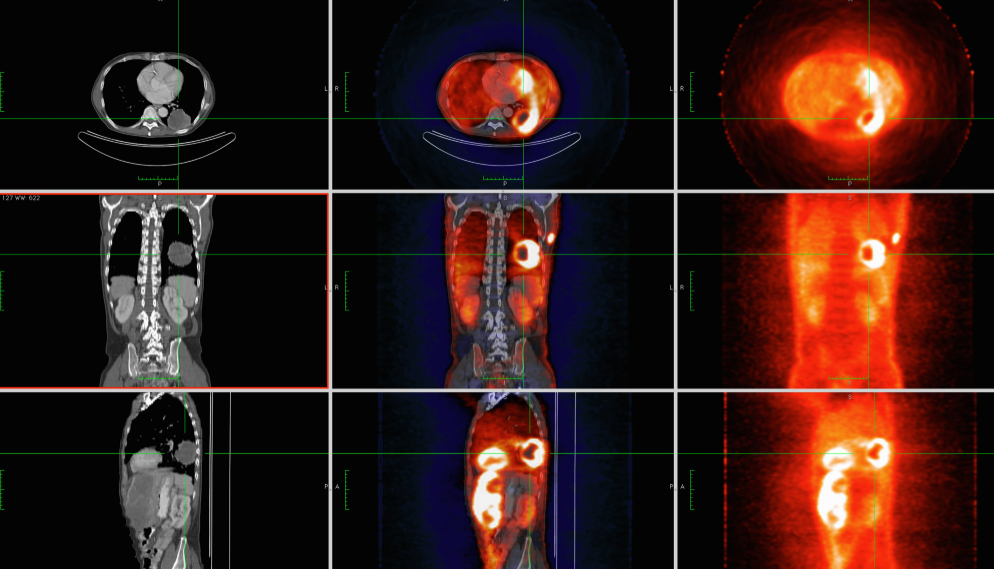
What is a PET Scan? A PET scan, or positron emission tomography scan, is an advanced medical imaging method used to observe metabolic processes in the body. This powerful tool provides doctors with insights into how organs and tissues function, making it invaluable for diagnosing and monitoring various conditions. Unlike traditional imaging techniques that focus on structure, a PET scan highlights activity at a cellular level, offering a deeper understanding of a patient’s health.
What is a pet scan?
How Does a PET Scan Work
A PET scan begins with the administration of a small amount of radioactive material called a tracer. This tracer is typically injected into the bloodstream, where it travels to areas of the body with heightened activity. The tracer emits positrons, which interact with electrons to produce gamma rays. These rays are detected by the PET scanner, which then creates detailed images of the body.
The images produced reveal patterns of metabolic activity, making it possible to identify abnormalities that might not be visible through other forms of imaging. For example, a tumor may show up more prominently on a PET scan due to its higher metabolic rate compared to surrounding tissues.
Key Uses of PET Scans
PET scans are used in a variety of medical fields, each with its unique applications.
Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Cancer detection and management rely heavily on PET scans. They help identify tumors, determine the stage of cancer, and monitor treatment progress. Tumors typically exhibit higher metabolic activity, making them easier to detect.
what is a pet scan? Neurological Disorders
In neurology, PET scans provide critical insights into brain function. They are used to diagnose conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, epilepsy, and Parkinson’s disease. Abnormal patterns in brain activity can be identified and studied, leading to better treatment strategies.
Heart Health Assessment
For cardiology, PET scans assess the health of the heart by analyzing blood flow and detecting damaged areas of heart tissue. They are particularly useful in diagnosing coronary artery disease and evaluating whether heart tissue can recover after injury.
What to Expect During a PET Scan
Preparation
Preparation for a PET scan usually involves fasting for several hours to ensure accurate results. What is a pet scan Depending on the area being examined, additional instructions may be provided by the medical team.
Administering the Tracer
The procedure begins with the injection of the tracer. Patients then wait for 30 to 60 minutes as the tracer spreads throughout the body.
The Scan
The patient lies on a table that moves through the PET scanner. The scan itself is painless and typically takes about 20 to 40 minutes.
After the Scan
After the scan, patients are encouraged to drink plenty of water to help flush the tracer from their system. The radioactive material naturally leaves the body within 24 hours.
Benefits of PET Scans
Early Detection to know What is a PET Scan
One of the most significant advantages of a PET scan is its ability to detect diseases early. By identifying abnormal metabolic activity, PET scans can reveal issues before structural changes occur.
Monitoring Treatment Effectiveness
PET scans are excellent for tracking how well treatments are working. For cancer patients, this means doctors can track how a tumor responds to therapy and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Functional Insights
The functional insights provided by PET scans set them apart from other imaging techniques. While CT or MRI scans focus on anatomical details, PET scans highlight how the body is functioning.
Are PET Scans Safe?
PET scans are considered safe for most individuals. The amount of radiation exposure is minimal and well within acceptable limits. However, pregnant or breastfeeding women should discuss potential risks with their healthcare provider.
Rarely, some individuals may experience mild allergic reactions to the tracer. These reactions are uncommon, and medical professionals are prepared to manage them if they occur.
Limitations of PET Scans
While PET scans are highly effective, they are not without limitations. The procedure can be expensive, and not all facilities are equipped to perform them.
In some cases, the resolution of PET images may not provide precise anatomical details. To overcome this, many facilities use hybrid imaging systems like PET/CT or PET/MRI, which combine the strengths of multiple modalities.
Strict preparation requirements, such as fasting, may not be suitable for all patients. Additionally, the radioactive tracer has a short half-life, meaning timing is critical for accurate imaging.
Advancements in PET Scan Technology
The field of PET imaging is continually evolving. Modern scanners now combine PET with CT or MRI, offering unparalleled diagnostic accuracy. These hybrid systems provide both functional and structural information, making them a cornerstone in advanced medical diagnostics.
Research into new tracers is also expanding the applications of PET scans. Specialized tracers can target specific diseases more effectively, opening doors for better diagnosis and treatment of conditions like autoimmune disorders and rare cancers.
Why PET Scans Are Important
PET scans have revolutionized the way doctors diagnose and treat diseases. By focusing on metabolic processes, they provide unique insights that other imaging techniques cannot match.
For patients, this means earlier detection of diseases, more precise diagnoses, and better monitoring of treatment progress. PET scans have become an essential tool in modern medicine, offering hope and clarity for countless individuals.