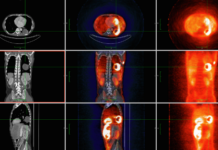
A PET scan 2, or Positron Emission Tomography scan, is an advanced imaging technique that plays a crucial role in diagnosing various medical conditions. It allows doctors to examine the functionality of organs and tissues within the body, providing valuable insights that traditional imaging methods like X-rays or CT scans cannot offer. In this article, we will explore what a PET can 2 is, how it works, and the potential benefits and risks associated with this medical procedure.

Understanding What a Scan Is
A PET scan is a non-invasive imaging technique used to observe the activity of cells in the body. Unlike other imaging techniques that only show the structure of organs, a PET scan reveals how organs and tissues are functioning. The test uses a small amount of radioactive material, known as a radiotracer. Which is injected into the bloodstream. This radiotracer emits positrons. Which are detected by the scanner to create images that reflect the metabolic activity of tissues.
This imaging method is particularly useful for detecting abnormalities in organs like the brain, heart, and cancerous tissues. It helps doctors assess the severity of conditions, track disease progression, and guide treatment decisions.
How Does a PET Scan Work?
The PET scan 2 process involves the introduction of a radiotracer into the body, usually through an intravenous injection. The radiotracer is designed to be absorbed by the tissues and organs that are being studied. Once injected, the radiotracer emits small particles called positrons, which interact with electrons in the body, producing gamma rays. These gamma rays are detected by the PET scanner, which converts the data into detailed images.
The scanner’s computer then processes these signals and creates a 3D image of the area being studied. The resulting images provide a clear representation of how the tissues or organs are functioning, which is especially important when diagnosing certain diseases.

Common Uses of a PET Scan
PET scans are commonly used in the medical field to diagnose and monitor various health conditions. Some of the primary uses include:
- Cancer Detection and Monitoring. PET scans are widely used to detect and monitor cancer. They can identify cancerous cells and assess the spread of the disease. PET scan 2 also help evaluate the effectiveness of cancer treatments by comparing the metabolic activity before and after treatment.
- Brain Disorders: PET scans are useful in detecting brain disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, epilepsy, and other neurological conditions. By studying brain activity, doctors can better understand how these diseases are affecting the brain and determine the most effective treatment plans.
- Heart Disease: PET scans help assess blood flow and heart function, which is essential for diagnosing heart diseases. It can detect areas of the heart that are not receiving enough blood, such as in cases of coronary artery disease.
- Infections and Inflammation. In some cases, PET scans are used to detect infections or areas of inflammation within the body. The scan helps doctors pinpoint where the infection or inflammation is located, enabling targeted treatment.
The Benefits of a PET Scan
PET scans offer several advantages over other imaging methods. These include:
- Non-Invasive and Painless: PET scans are non-invasive, meaning they do not require any surgery or incisions. The procedure is generally painless and does not involve any discomfort for the patient.
- High Sensitivity: PET scans are highly sensitive and can detect abnormal metabolic activity at an early stage, making them valuable for early diagnosis. This allows doctors to intervene and start treatment promptly.
- Comprehensive Imaging: Unlike traditional imaging methods that primarily show the structure of organs, PET scans provide functional information, allowing for a more accurate diagnosis.
- Monitoring Disease Progression: PET scans are particularly useful for monitoring the progression of diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer’s. By tracking changes in metabolic activity over time, doctors can assess the effectiveness of treatments and make adjustments as needed.
- Personalized Treatment: The ability to visualize how the body’s organs and tissues are functioning helps doctors tailor treatments to individual patients. PET scans allow for a more personalized approach to healthcare, ensuring that treatments are appropriate and effective.

Potential Risks and Limitations of PET Scan
While PET scans are generally safe, there are a few potential risks and limitations to consider. These include:
- Radiation Exposure: Although the amount of radiation used in a PET scan is low, it is still a form of exposure. Any pregnant and young children are typically advised. To avoid PET scans unless absolutely necessary due to the potential risks associated with radiation exposure.
- Allergic Reactions: In rare cases, patients may experience allergic reactions to the radiotracer used in the scan. These reactions are typically mild but should be monitored by healthcare providers.
- Cost: PET scans can be expensive, and not all insurance plans may cover the cost. This may make it inaccessible for some patients who need the procedure for diagnostic purposes.
- Not Always Available. PET scanners are not as widely available as other imaging equipment, and the procedure may not be offered at all healthcare facilities. Patients may need to travel to specialized centers to undergo a PET scan.
Preparing for a PET Scan
Before undergoing a PET scan, patients will be provided with instructions on how to prepare. These may include:
- Fasting. In some cases, patients may be required to fast for several hours before the scan. This ensures that the radiotracer is absorbed properly and does not interfere with food intake.
- Medications. Some medications may need to be temporarily stopped before the scan. Patients should inform their doctor of any medications they are taking to ensure the procedure goes smoothly.
- Comfortable Clothing. It is recommended that patients wear loose, comfortable clothing for the scan, as they may be required to lie still for extended periods during the procedure.

What Happens During the PET Scan?
During the PET scan, the patient will be asked to lie down on a table that moves into the scanner. The scanner will rotate around the patient, capturing detailed images of the body. The scan typically takes between 30 minutes and an hour, depending on the area being studied. Patients are asked to remain still during the scan to ensure clear, accurate images.
Conclusion: The Role of PET Scans in Modern Medicine
In conclusion, a PET scan 2 is a powerful diagnostic tool that helps doctors assess the functionality of organs and tissues within the body. It provides detailed images that allow for early detection and precise monitoring of various diseases, including cancer, heart conditions, and neurological disorders. While there are some risks and limitations, the benefits of PET scans in terms of early diagnosis, personalized treatment, and monitoring make them an invaluable tool in modern medicine. As technology continues to advance, PET scans are likely to become even more refined and accessible, further enhancing their role in healthcare.
For more information about advanced diagnostic techniques and healthcare solutions, visit Health Illusion and Biotul.